What Is Software? A Complete Guide for 2025
Updated on : 16 April 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Every digital device you use—whether it’s a smartphone, laptop, or even your smart refrigerator—relies on software to function. This guide explores the world of software, making it accessible to beginners and insightful for tech enthusiasts.
What Is Software?
Software is essentially a set of instructions, or a program, that directs a computer to perform specific operations. Unlike hardware, which you can physically touch, software is intangible. Think of it as the intelligence that brings hardware to life, enabling everything from simple tasks to complex artificial intelligence.
Software: The non-tangible set of instructions that commands a computer to perform specific tasks.

Image Source: Generated/Attribution
Types of Software
Let’s break down the main categories of software:
- Application Software: Designed for end-users to perform specific tasks. Examples include Microsoft Office, Adobe Photoshop, and mobile games.
- System Software: Manages and controls computer hardware so that application software can run. Operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux fall into this category.
- Programming Software: Provides tools for developers to write, test, and debug code. Examples include Visual Studio, Eclipse, and Xcode.
- Middleware: Connects different software systems, allowing them to communicate and exchange data. This is crucial for enterprise applications.
- Driver Software: Enables the operating system to communicate with hardware devices like printers, graphic cards, and USB drives.

Need help choosing the right software for your project?
Consider exploring our Manual Testing Services to validate the effectiveness of your database security measures.
| Type | Purpose | Examples | Real-World Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application Software | Performs user-specific tasks | Microsoft Word, Chrome, Mobile Games | Writing documents, browsing the web, entertainment |
| System Software | Manages hardware and provides platform for apps | Windows, Linux, Android | Operating computers, smartphones, and tablets |
| Programming Software | Tools for writing and debugging code | Visual Studio, Eclipse, Xcode | Developing new applications and software |
| Middleware | Connects different applications | WebSphere, MuleSoft | Ensuring different business systems can communicate with each other |
| Driver Software | Enables communication with hardware | Printer Drivers, GPU Drivers | Allowing computers to use printers and graphic cards |
How Does Software Work?
Software is created using programming languages. The code is then compiled or interpreted into machine-readable instructions that the computer's processor can execute. When you launch an application, the software sends signals to the hardware, telling it what to do, from displaying images to processing data.
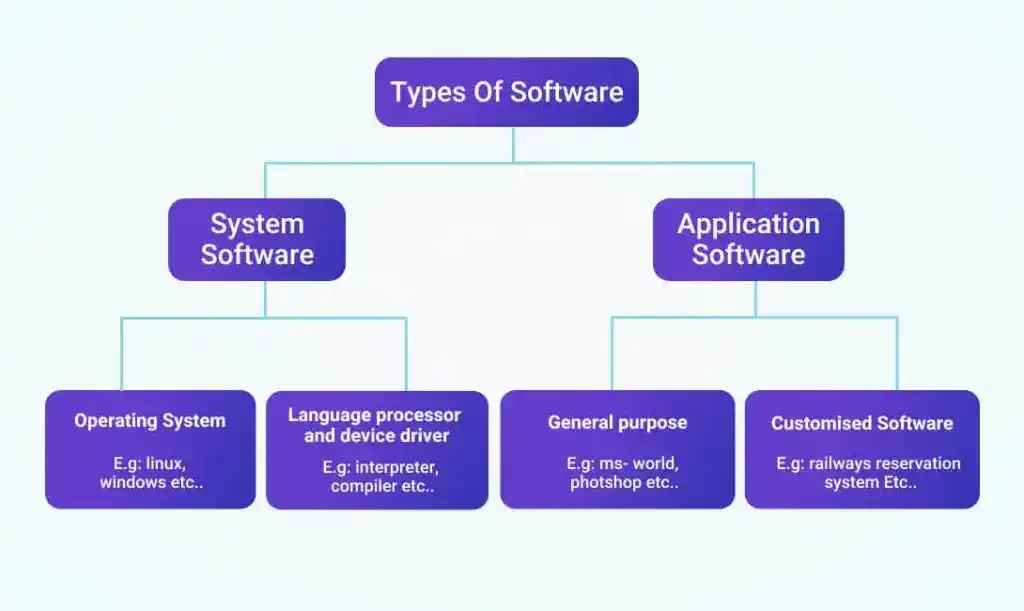
Image Source: Generated/Attribution
Software vs. Hardware: Key Differences
| Aspect | Software | Hardware |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set of instructions/programs | Physical components |
| Tangibility | Intangible (code, data) | Tangible (chips, screens, etc) |
| Function | Tells hardware what to do | Executes instructions |
| Changeability | Easily updated or modified | Harder to change or replace |
| Cost | Varies, often subscription-based or one-time purchase | Significant upfront investment |
The Evolution of Software
- Early Days: Software was closely tied to specific hardware, with programs written for individual machines.
- 1980s–2000s: The rise of personal computers led to software being distributed on physical media like floppy disks and CDs.
- Today: Cloud computing and digital distribution have made software more accessible and updateable than ever before.
Consider exploring our Cloud Computing Services to stay ahead.
How Is Software Distributed?
Software distribution methods have evolved significantly:
- Direct Downloads: From vendor websites.
- App Stores: Centralized platforms like Apple's App Store and Google Play.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Software as a Service (SaaS) delivered over the internet.
- Open-Source Repositories: Platforms like GitHub allow developers to share and collaborate on code.

Looking for custom software development or cloud solutions?
Trends in Software for 2025
- AI-Driven Software: Integration of artificial intelligence for automation and personalized experiences.
- Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: Tools that allow non-programmers to build applications.
- Cross-Platform Development: Software that runs on multiple operating systems and devices.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity: Increased focus on security to protect against cyber threats.
- Cloud-Native Applications: Designed to leverage the scalability and flexibility of cloud environments.
Check out our Web Application Development Services to see how we can help you implement these trends.

Image Source: Generated/Attribution
The Impact of Software on Daily Life
Software impacts nearly every aspect of modern life:
- Communication: Apps like WhatsApp and Zoom connect people globally.
- Entertainment: Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify provide endless entertainment options.
- Productivity: Tools like Microsoft Office and Slack enhance work efficiency.
- Healthcare: Software manages patient records and supports medical research.
- Transportation: GPS navigation systems and ride-sharing apps have transformed how we travel.
Concluding Thoughts
Software is the invisible engine behind the digital world. From operating systems to mobile apps, it powers every modern device and service. Understanding what software is—and how it evolves—helps you make better choices as a user, business owner, or developer.
FAQs
Q.1. What is software?
A: Software is a collection of instructions or programs that tell a computer how to perform tasks, enabling everything from web browsing to gaming.
Q.2. What are the main types of software?
A: The main types are application software, system software, programming software, middleware, and driver software.
Q.3. How is software different from hardware?
A: Software is intangible and controls the actions of hardware, which is the physical part of a computer.
Q.4. How is software distributed today?
A: Most software is downloaded online or accessed through cloud platforms and app stores.
Q.5. What trends are shaping software in 2025?
A: Cloud-native development, AI integration, low-code platforms, cross-platform compatibility, and enhanced security.


