What is Cloud Computing?
Updated on : 23 October, 2024, 12:20 IST

Image Source: Freepik.com
Table Of Contents
Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses and individuals access and manage technology resources. By leveraging the internet, cloud computing provides on-demand access to a wide array of computing services, including storage, processing power, and applications. This shift from traditional on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based solutions offers numerous benefits, making it an essential component of modern IT strategy.
What is Cloud Computing?
At its core, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet. This includes everything from virtual servers and storage to software applications. Instead of relying on local servers or personal devices, users can access these resources remotely through a network of data centers managed by cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
-
On-Demand Self-Service : Users can provision computing resources automatically without requiring human interaction with service providers
-
Broad Network Access : Services are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use across various platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops).
-
Resource Pooling: The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model.
-
Rapid Elasticity : Resources can be elastically provisioned and released to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand.
-
Measured Service: Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service
Types of Cloud Computing Services
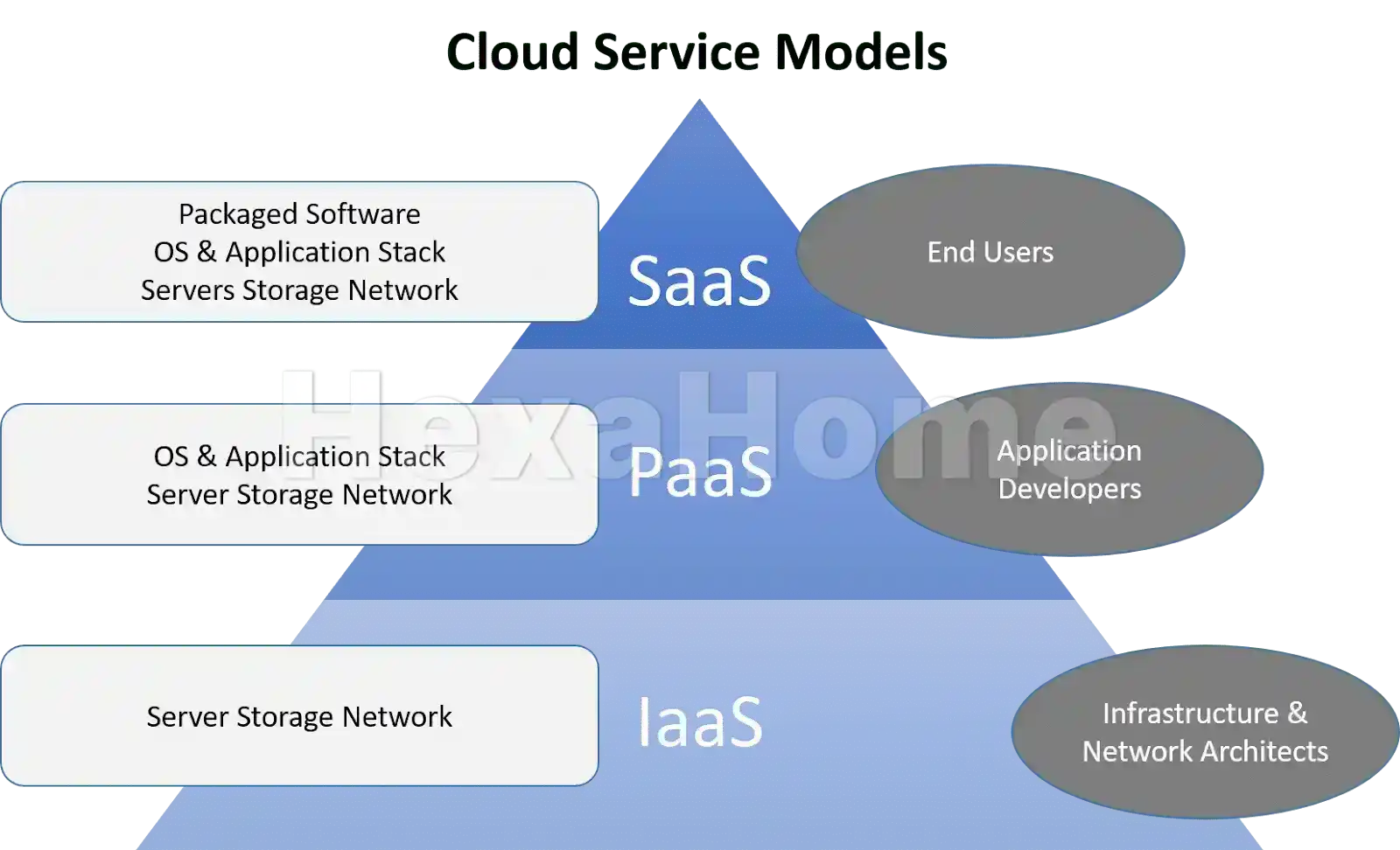
Image Source: uniprint.net
Cloud computing is typically categorized into three main service models:
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent servers and storage as needed. Examples include AWS EC2 and Google Compute Engine Learn more
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers hardware and software tools over the internet, typically for application development. Users can develop applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Learn more
-
Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Examples include Google Workspace and Salesforce. Learn more
Deployment Models of Cloud Computing
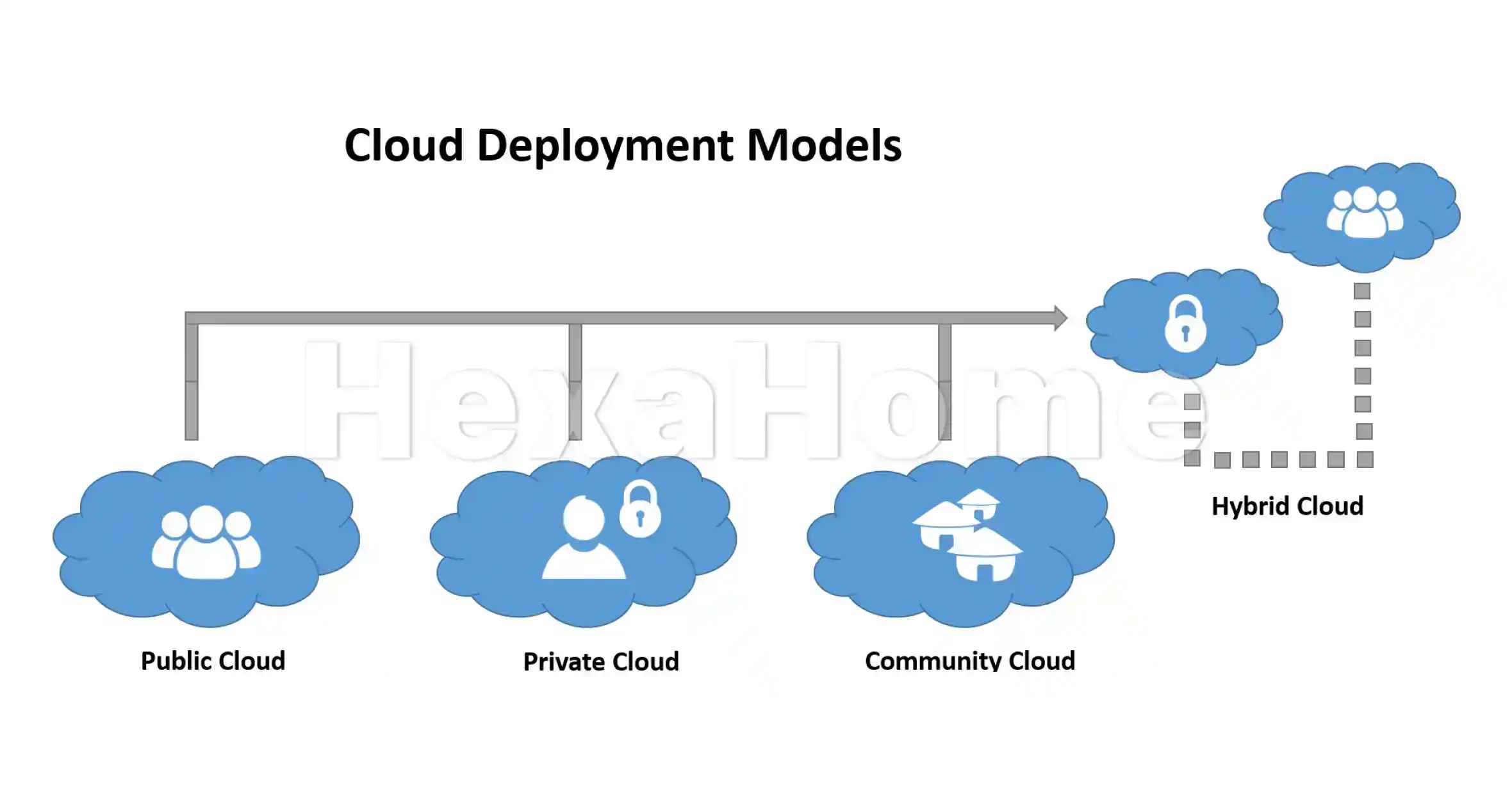
Image Source: uniprint.net
Cloud computing can be deployed in several ways, each offering different levels of control, flexibility, and security:
-
Public Cloud: Services are delivered over the public internet and shared across multiple organizations. This model is cost-effective but may raise security concerns.
-
Private Cloud: Dedicated to a single organization, providing greater control and security but at a higher cost.
-
Hybrid Cloud: Combines both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them for greater flexibility.
-
Multi-Cloud: Utilizes services from multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance redundancy
Benefits of Cloud Computing
-
Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for heavy upfront investments in hardware; users pay only for what they use.
-
Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand without significant delays or costs.
-
Flexibility: Access resources from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration.
-
Disaster Recovery: Enhanced backup solutions ensure data is safe and accessible even in emergencies
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many advantages, cloud computing also presents challenges:
-
Security Risks: Storing data off-site raises concerns about data breaches and loss of control.
-
Downtime: Reliance on internet connectivity means that service outages can disrupt access to critical applications.
-
Compliance Issues: Organizations must ensure that their cloud usage complies with relevant regulations regarding data protection
The Future of Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing looks promising with emerging trends such as:
-
Edge Computing: Bringing computation closer to data sources to reduce latency.
-
Artificial Intelligence Integration: Enhancing cloud services with AI capabilities for better analytics and automation.
-
Increased Focus on Security: As cyber threats evolve, cloud providers are investing heavily in advanced security measures
Summing it Up
Cloud computing is not just a trend; it represents a fundamental shift in how organizations operate. By embracing cloud technologies, businesses can enhance their agility, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. As technology continues to advance, understanding cloud computing will be crucial for anyone looking to thrive in an increasingly digital world.


