Micro Frontend Architecture for Modular Web Apps
Updated on : 8 May 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Definition and concept of micro frontends
- 3. Popular organizations utilizing micro frontend strategies
- 4. Key principles behind micro frontend architecture
- 5. Benefits of adopting micro frontend structures
- 6. Ideal scenarios for applying micro frontends
- 7. The internal workings of micro frontend systems
- 8. Steps to build a micro frontend solution
- 9. Challenges involved in micro frontend adoption
- 10. Tools and frameworks that support micro frontend development
- 11. Security considerations for micro frontends
- 12. Performance optimization in micro frontend applications
- 13. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Micro Frontend Architecture for Modular Web Apps breaks down large applications into smaller, independent modules, each developed by different teams. This approach enhances scalability, speeds up deployment, and allows for technology diversity, enabling efficient and flexible web app development.
Definition and concept of micro frontends

Image Source: google
| 🔄 Stage | 📌 Description |
|---|---|
| Micro Frontends | An architectural style that decomposes a frontend application into smaller, independently deployable modules. |
| Modularity | Breaking down a large frontend application into smaller, manageable, and maintainable parts. |
| Independent Deployment | Each micro frontend can be deployed, updated, and scaled independently of others. |
| Technology Agnostic | Different micro frontends can be built using different technologies or frameworks, allowing flexibility. |
| Loose Coupling | Micro frontends interact through well-defined APIs, ensuring minimal dependency between them. |
| Integration | Micro frontends are integrated into the final application through composition techniques like web components or iframes. |
| Scalability | Since each module is independent, the application can scale both in terms of development and runtime. |
| User Experience | Despite being split into smaller pieces, the user experiences a seamless interface. |
Popular organizations utilizing micro frontend strategies
| 🏢 Organization | 📌 Use of Micro Frontends |
|---|---|
| Spotify | Uses micro frontends to separate different parts of their UI like search, playlists, and user profile. |
| Netflix | Uses micro frontends to scale its UI components and reduce dependencies between teams. |
| Zalando | Adopted micro frontends to enable multiple teams to work on different sections of their online store independently. |
| Ikea | Uses micro frontends to split their e-commerce platform into manageable, independently deployable parts. |
| BMW | Leverages micro frontends to streamline development across various parts of their digital ecosystem. |
| PayPal | Utilizes micro frontends to enable separate teams to focus on different features in their payment system. |
Key principles behind micro frontend architecture
Micro Frontend Architecture for Modular Web Apps is a modern approach to building large-scale applications by dividing the frontend into smaller, manageable pieces. Below are the key principles:
- 🧩 Modularity
- The app is split into feature-based, independent modules.
- Each module represents a part of the UI with its own logic and styling.
- 🚀 Independent Deployment
- Micro frontends are built and deployed separately.
- Teams can release updates without affecting the whole app.
- ⚙️ Technology Agnostic
- Different teams can use different technologies React, Vue, Angular, etc..
- Promotes flexibility in choosing the right tools.
- 🧬 Loose Coupling
- Components have minimal dependencies.
- They interact through APIs or custom events.
- 🔗 Seamless Integration
- All micro frontends combine into a unified user interface.
- Methods include web components, iframes, or build-time bundling.
- 👥 Team Autonomy
- Each team owns a micro frontend end-to-end.
- Encourages faster development and independent scaling.
- 🎯 Focused Ownership
- Teams are responsible for development, testing, and deployment of their modules.
- Ensures accountability and quality.

you want to hire Frontend Developer?
Benefits of adopting micro frontend structures
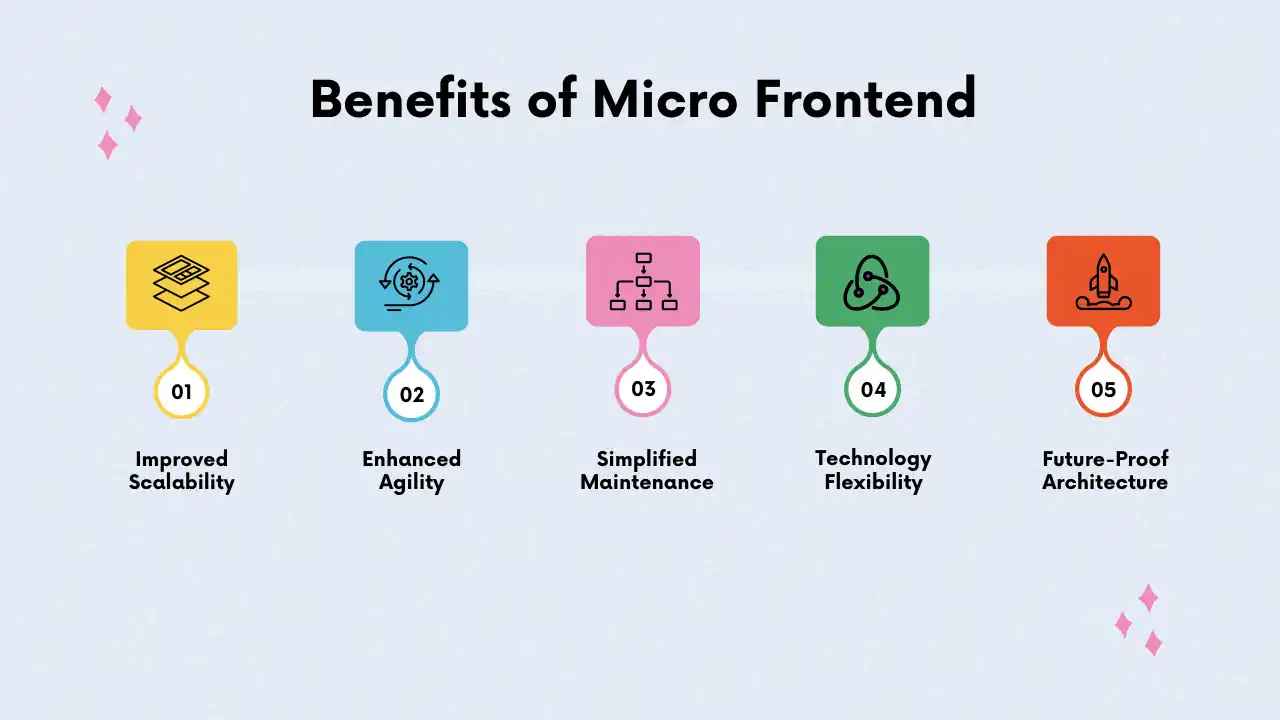
Image Source: google
| ✅ Benefit | 📌 Description |
|---|---|
| Team Autonomy | Different teams can work independently on separate features or modules. |
| Scalability | Easier to scale development and deployment processes across large teams. |
| Faster Deployment | Updates can be deployed to individual parts of the app without full redeployment. |
| Technology Flexibility | Teams can choose different frameworks or tools best suited to their feature. |
| Improved Maintainability | Smaller codebases are easier to maintain, test, and debug. |
| Parallel Development | Multiple teams can work in parallel, reducing development time. |
| User Experience Consistency | Each module is integrated seamlessly to ensure a smooth UI/UX. |
| Reduced Risk | Isolated changes reduce the chance of breaking the entire application. |
Empower Your Business with Frontend Web Solutions with Hexadecimal Software
Ideal scenarios for applying micro frontends
| 📌 Scenario | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| Large-Scale Applications | When the frontend is too big for a single team to manage efficiently. |
| Multiple Teams Working Together | Ideal when different teams are responsible for different features or sections. |
| Frequent Independent Deployments | Useful when parts of the app need frequent updates without affecting others. |
| Diverse Tech Stacks | When teams want to use different frameworks or libraries for their features. |
| Gradual Migration | Helpful for slowly moving from a monolithic frontend to a modular structure. |
| Need for Faster Time-to-Market | Enables faster releases by allowing parallel development and deployment. |
You Might Also Like
The internal workings of micro frontend systems
Micro Frontend Architecture for Modular Web Apps organizes frontend development by splitting the UI into small, independently managed pieces. Here's how it works internally:
- 📦 Independent Codebases
- Each micro frontend has its own repository, build process, and deployment pipeline.
- Teams can develop and maintain features separately.
- 🔗 Integration Layer
- A shell or container app loads and integrates all micro frontends.
- Integration can happen at runtime (via dynamic imports) or build time.
- 📡 Communication Between Micro Frontends
- Modules communicate through custom events, shared state, or APIs.
- Ensures loose coupling and independence.
- 🧪 Isolated Testing & Deployment
- Each micro frontend can be tested and deployed individually.
- Reduces risk and improves reliability.
- 🧬 Shared Components and Utilities
- Common UI components or helper libraries are shared via package managers.
- Keeps consistency across different modules.
- 🌍 Routing Management
- The container or host application manages global routing.
- Each micro frontend handles internal navigation.
By adopting Micro Frontend Architecture for Modular Web Apps, organizations gain flexibility, maintainability, and speed, especially in large-scale projects.
Steps to build a micro frontend solution
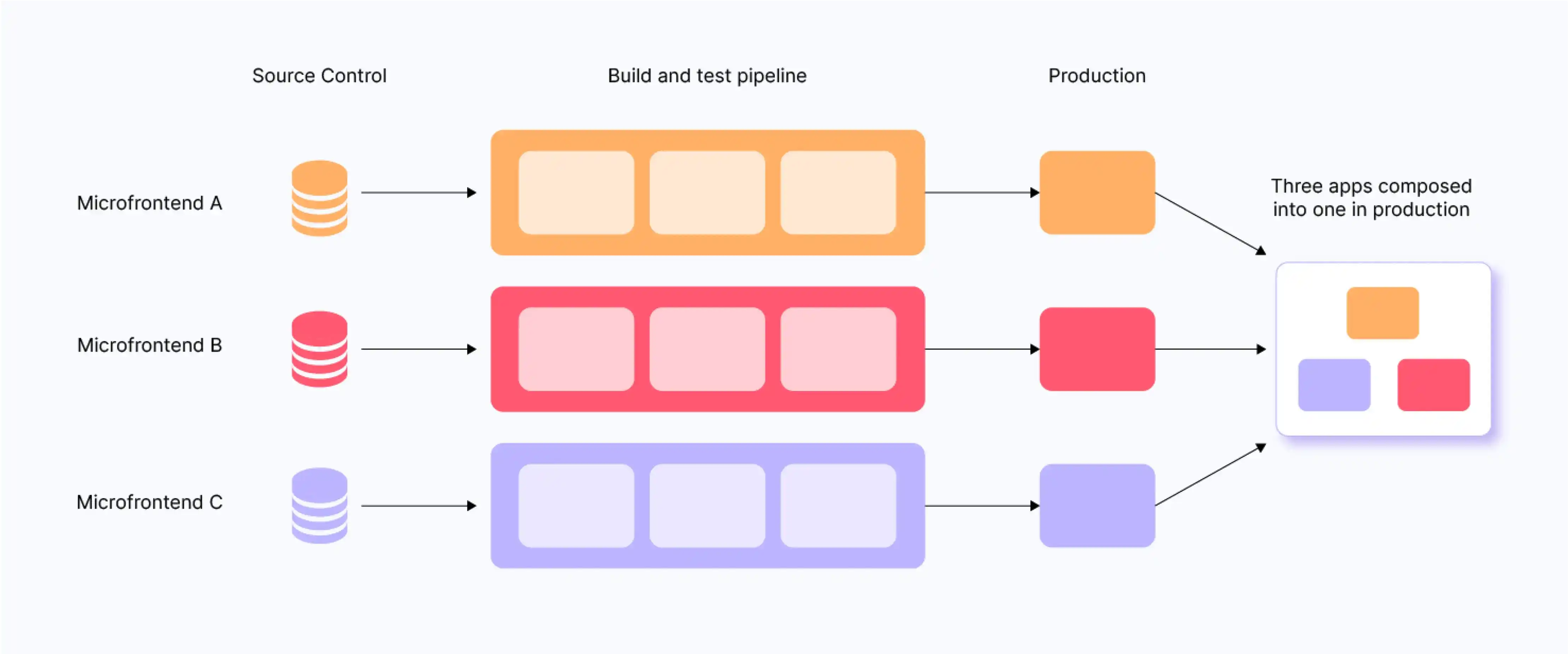
Image Source: google
| 🛠️ Step | 📌 Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Split the App | Break the app into small, feature-based parts. |
| 2. Assign Teams | Give each part to a separate team. |
| 3. Pick Integration Method | Choose how parts will come together (e.g., Web Components, iframes). |
| 4. Create Separate Codebases | Each part has its own code and setup. |
| 5. Build and Deploy | Build and launch each part on its own. |
| 6. Share Common Styles | Use a shared design or style guide. |
| 7. Manage Routing | Set up navigation between parts. |
| 8. Connect the Parts | Use events or APIs if parts need to talk to each other. |
| 9. Test Everything | Test each part and the whole app together. |
Challenges involved in micro frontend adoption
While Micro Frontend Architecture for Modular Web Apps offers many benefits, it also comes with some challenges:
- 🔗 Integration Complexity
- Combining multiple micro frontends can be tricky, especially when using different frameworks.
- ⚙️ Performance Overhead
- Loading many separate bundles may slow down the app if not optimized properly.
- 🎨 Consistent Design
- Ensuring a uniform look and feel across all micro frontends can be difficult.
- 🧪 Testing Difficulties
- Testing individual parts is easy, but testing the full app together requires extra effort.
- 📦 Shared Dependencies
- Managing common libraries or versions across teams can lead to conflicts.
- 🧠 Steeper Learning Curve
- Teams need to learn new patterns and tools to work with micro frontends effectively.
- 🚦Routing and State Management
- Handling global routing and shared state adds complexity.
Despite these challenges, with proper planning and tooling, Micro Frontend Architecture for Modular Web Apps can still be a powerful solution for scaling frontend development.
Tools and frameworks that support micro frontend development
| 🛠️ Tool/Framework | 📌 Purpose |
|---|---|
| Module Federation (Webpack 5) | Shares code and loads micro frontends at runtime. |
| Single-SPA | Combines multiple frontend apps into one seamless app. |
| Qiankun | A micro frontend framework based on Single-SPA with easier setup. |
| Web Components | Allows building framework-agnostic custom HTML elements. |
| Import Maps | Loads JavaScript modules from different sources in the browser. |
| Nx | Monorepo tool that helps manage multiple frontend projects together. |
| Bit | Lets teams share and collaborate on components across projects. |
| FrintJS | Framework for building modular, reactive micro frontends. |

Looking Web App Developer For your business?
Security considerations for micro frontends

Image Source: google
| 🔒 Security Area | 📌 Consideration |
|---|---|
| Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) | Set proper CORS policies to control access between services. |
| Authentication | Ensure each micro frontend verifies the user's identity securely. |
| Authorization | Restrict access to features based on user roles and permissions. |
| Content Security Policy (CSP) | Use CSP headers to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. |
| Input Validation | Always validate user input on both frontend and backend. |
| Dependency Management | Keep third-party packages up-to-date to avoid known vulnerabilities. |
| Secure Communication | Use HTTPS and secure tokens (e.g., JWT) for all data transfers. |
| Isolation | Run micro frontends in isolation (e.g., via iframes or sandboxing) when needed. |
Transform Your Business with Custom Progressive Web App Development
Performance optimization in micro frontend applications
To ensure Micro Frontend Architecture for Modular Web Apps performs efficiently, the following optimization strategies are essential:
- ⚙️ Lazy Loading
- Load micro frontends only when needed, reducing initial load time.
- Use techniques like code splitting to load parts dynamically.
- 📦 Bundle Optimization
- Keep micro frontends' bundles small to reduce the size of the overall app.
- Use tools like Webpack to optimize and minimize the code.
- 💡 Efficient Communication
- Minimize inter-micro frontend communication to reduce overhead.
- Use lightweight APIs or shared state for smooth interaction.
- 🔄 Caching
- Cache micro frontends and their assets to avoid unnecessary reloading.
- Use browser caching and service workers for offline capabilities.
- 🌍 Global Styles Management
- Reduce the impact of shared global styles across micro frontends.
- Use scoped styles or CSS modules to prevent style conflicts.
- ⚡ Optimize Rendering
- Avoid unnecessary re-renders in micro frontends.
- Use libraries like React’s
memoor Vue’sv-onceto optimize rendering performance.
By adopting these strategies, Micro Frontend Architecture for Modular Web Apps can maintain high performance even at scale.
FAQs
Q.1. What are micro frontends?
A : Micro frontends break up a monolithic frontend into smaller, independent, and reusable pieces, each owned by different teams.Q.2. Why use micro frontends?
A : To enable independent development, scaling, and deployment of different parts of a frontend app by separate teams.Q.3. How do micro frontends communicate?
A : They communicate via APIs, events, or shared state, depending on the integration strategy.Q.4. Can different micro frontends use different technologies?
A : Yes, micro frontends are technology-agnostic and can use different frameworks or libraries as needed.Q.5. How do micro frontends get integrated?
A : They are integrated at runtime or build time using techniques like Web Components, iframes, or Module Federation.Q.6. What are the challenges of micro frontends?
A : Key challenges include integration complexity, ensuring consistent design, managing shared dependencies, and handling routing.Q.7. How do you deploy micro frontends?
A : Each micro frontend is deployed independently, allowing for faster and more flexible releases without affecting the whole app.Q.8. What tools support micro frontends?
A : Tools like Webpack Module Federation, Single-SPA, and Qiankun help manage and integrate micro frontends.





