How to Build Customs Lims Software
Updated on : 28 February, 2025

Image Source: Proton
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What is a LIMS and Why Choose a Custom Build?
- 3. 3 Major Benefits of Adopting a Healthcare LIMS
- 4. How Does a LIMS Work? A Step-by-Step Overview
- 5. Essential LIMS Capabilities and Features
- 6. Building a Custom LIMS: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 7. LIMS Development Costs: Factors and Considerations
- 8. Challenges of LIMS Adoption and Mitigation Strategies
- 9. Hexadecimal Software and LIMS
- 10. The Bottom Line
- 11. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
In today's data-driven healthcare landscape, laboratories are generating unprecedented volumes of information. Efficient and accurate management of this data is not just beneficial, it's critical, especially given stringent regulatory requirements. A Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is the solution. While commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) LIMS options exist, developing a custom LIMS provides the distinct advantage of tailoring the system precisely to your laboratory's unique needs, workflows, and data handling requirements.
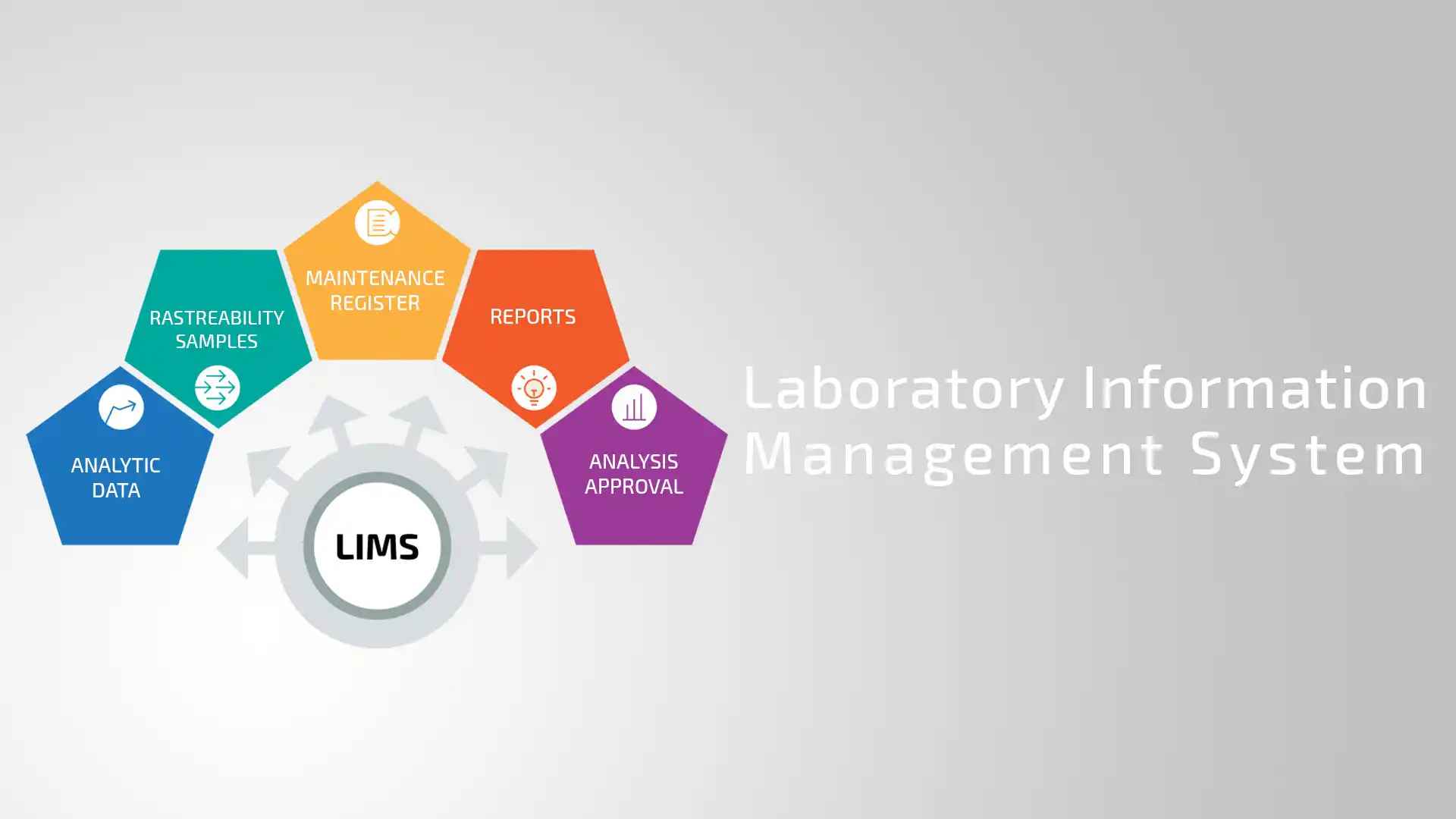
Image Source: google.com
What is a LIMS and Why Choose a Custom Build?
A LIMS is a software system meticulously designed to manage laboratory samples, associated data, and analytical workflows. It automates a wide range of tasks, from the initial sample registration and tracking to comprehensive reporting and secure archiving. The adoption of LIMS is rapidly increasing, as evidenced by market projections estimating a $2.1 billion global market by 2026.
In healthcare, the reliability of lab results is paramount. Consider that healthcare entities in the US conduct approximately 14 billion lab tests annually, with a staggering 70% of medical decisions hinging on these results. This underscores the acute need for robust and reliable LIMS solutions. The hospital LIMS market is projected to reach $4.90 billion by 2029, exhibiting a remarkable CAGR of 20.55%.
While pre-built LIMS offer a baseline functionality, custom LIMS offer significant advantages:
- Precision Tailoring: Custom LIMS solutions are architected to mirror your lab's specific processes, workflows, and data structures, resulting in optimized efficiency and reduced bottlenecks.
- Scalability and Adaptability: A custom LIMS is built to evolve alongside your laboratory's growth. You can incrementally add features, expand functionality, and adapt to changing regulatory landscapes without being constrained by the limitations of a commercial product.
- Seamless Integration: Custom LIMS can be designed for seamless integration with your existing array of instruments, software platforms, databases, and enterprise systems. This eliminates data silos and promotes a cohesive information ecosystem.
- Security and Compliance: A custom LIMS allows you to implement granular security controls and compliance features tailored to specific regulations (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR, CLIA), ensuring data integrity and patient privacy.

Streamline Healthcare Laboratory Workflows with Hexadecimal Software or LIS/LIMS
3 Major Benefits of Adopting a Healthcare LIMS
- Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency: By automating manual processes, a LIMS minimizes the risk of human error, accelerates turnaround times, and ensures data integrity.
- Comprehensive Integration Support: A well-designed LIMS facilitates seamless communication and data exchange between laboratory instruments, analytical platforms, and other critical systems.
- Streamlined Workflow Management: From sample accessioning to result reporting, a LIMS orchestrates the entire laboratory workflow, optimizing resource allocation, reducing delays, and improving overall productivity.
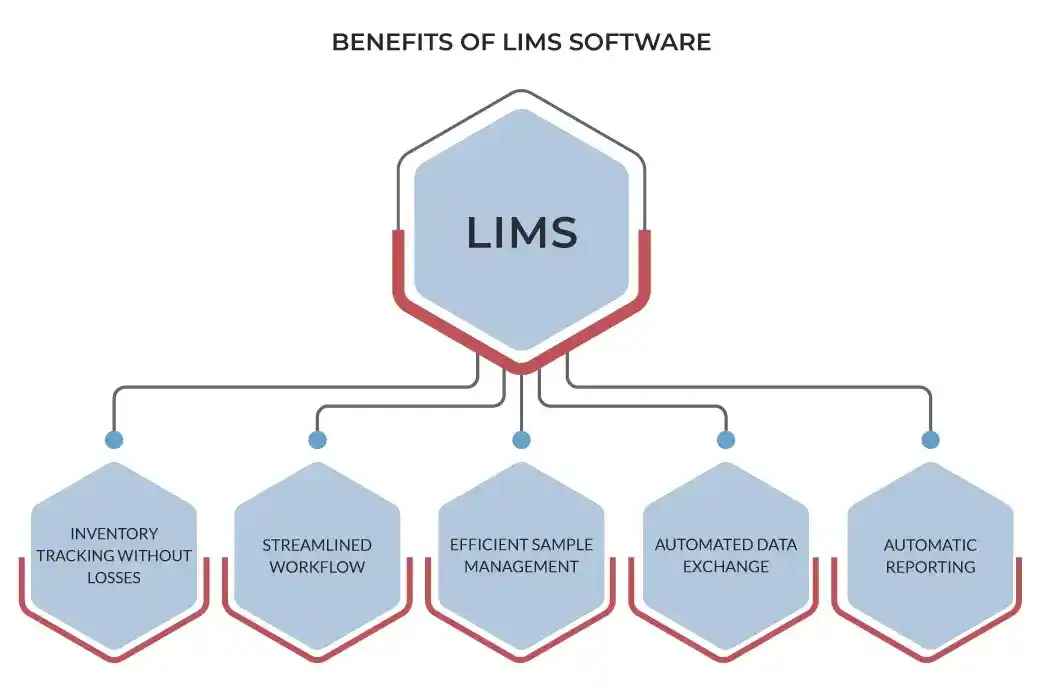
Image Source: google.com
How Does a LIMS Work? A Step-by-Step Overview
- Registration: Users, with appropriate credentials, log into the LIMS software, initiating the workflow.
- Preparation: The system begins internal processes, converting raw data into a structured format suitable for analysis. This stage may involve data cleansing, transformation, and validation.
- Allocation: The system intelligently allocates data to specific instruments, analytical tools, and personnel based on predefined workflows and user roles.
- Validation: Data originating from various sources is rigorously validated against established quality control parameters and sample metadata.
- Approval & Retesting: Validated data undergoes a review process, where qualified personnel approve the results for reporting. If anomalies or discrepancies are detected, the system initiates a retesting protocol.
- Reporting: The LIMS leverages pre-defined templates to generate comprehensive reports, incorporating sample data, analytical results, and relevant metadata. These reports can be printed, exported, or securely shared.
- Archiving: To ensure long-term data integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements, all relevant information is securely archived in a centralized data repository.
Essential LIMS Capabilities and Features
- Sample Management: Comprehensive tracking and management of samples throughout their lifecycle, from accessioning to disposal.
- Workflow Automation: Automated record-keeping and rule-based decision-making to minimize manual intervention and ensure consistent processes.
- Secure Data Storage: Robust data storage mechanisms with comprehensive security controls to protect sensitive information and ensure data integrity. Compliance with relevant data protection standards (e.g., HIPAA).
- Inventory & Instrument Management: Real-time tracking of reagents, consumables, and other inventory items, along with comprehensive instrument maintenance scheduling and logging.
- Advanced Analytics & Reporting: Powerful data analysis tools and customizable reporting capabilities to extract meaningful insights from laboratory data.
- Regulatory Compliance Modules: Built-in tools and features to support compliance with relevant regulatory standards, such as CLIA, HIPAA, and FDA 21 CFR Part 11.
Building a Custom LIMS: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Define Your IT System Requirements:
- Budget: Develop a comprehensive budget that encompasses software development, hardware infrastructure, ongoing maintenance, and technical support.
- Core Functions: Identify the core functionalities that are essential for supporting your laboratory's unique operations. Prioritize features based on their impact on efficiency, accuracy, and compliance.
- User Base: Determine the number of users who will require access to the LIMS, and define their respective roles and permissions.
- Sample Characteristics: Take into account the specific attributes of your lab samples.
-
Select a Development Partner: Carefully evaluate potential development partners based on their expertise in LIMS development, their understanding of the healthcare industry, and their track record of delivering successful projects.
-
Design the User Interface (UI): Design the graphical user interface (GUI) for the LIMS software.
-
Rigorous Software Testing: Perform thorough testing to ensure the LIMS software operates accurately.
-
Launch Preparation: Ensure the LIMS system is properly configured and integrated with existing IT infrastructure.
LIMS Development Costs: Factors and Considerations
The cost of developing a custom LIMS can vary significantly based on factors such as:
- System Complexity: The number of features, the level of customization, and the degree of integration with existing systems will all impact development costs.
- Development Team Expertise: The experience and skill of the development team will influence both the cost and the quality of the final product.
- Technology Stack: The choice of programming languages, databases, and other technologies can affect development costs.
- Data Migration Requirements: Migrating data from legacy systems can be a complex and time-consuming process.
As a general guideline:
- Basic Data Organization Module: $15,000 - $45,000 (3-6 weeks) for implementing basic sample inventory and data management capabilities.
- Process Automation Module: $30,000 - $70,000 for automating manual laboratory processes and workflows.
- Full Digital Transformation: $60,000 - $200,000+ (4-9 months) for developing a comprehensive LIMS solution that integrates multiple departments and supports advanced analytics.
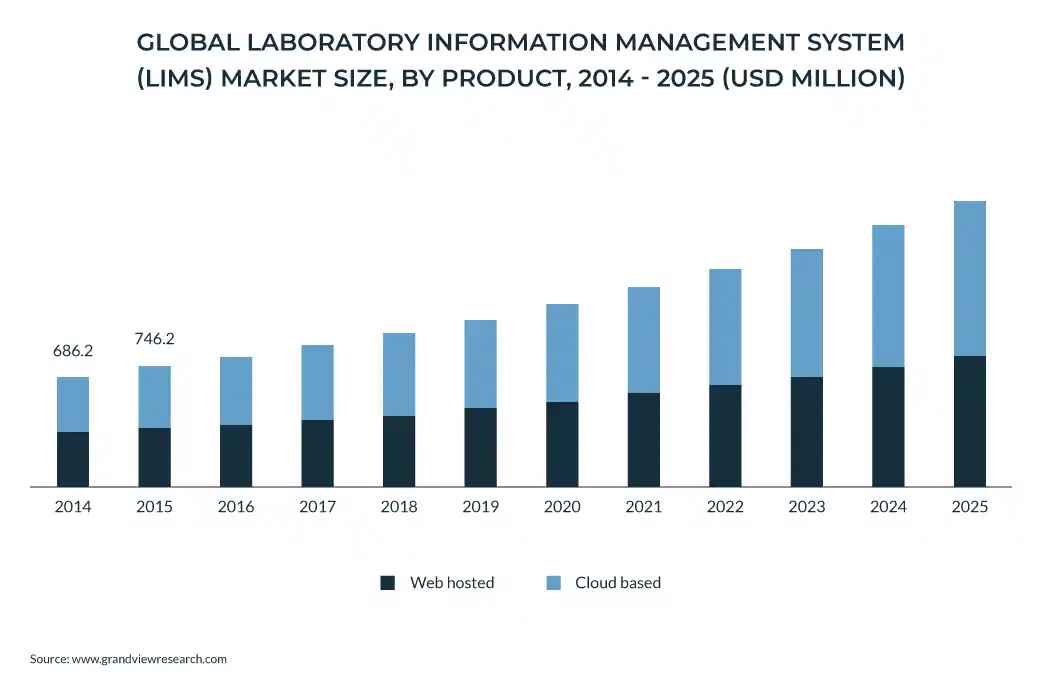
Image Source: google.com
Challenges of LIMS Adoption and Mitigation Strategies
- User Resistance: Implement a comprehensive change management strategy that involves end-users in the selection, design, and implementation process. Provide adequate training and support to ensure user adoption.
- Integration Complexities: Carefully plan the integration process, and select a LIMS platform with robust integration capabilities and support for industry-standard protocols.
- High Initial Costs: Consider a phased implementation approach, starting with core functionalities and gradually adding more advanced features as needed.
- Data Migration Risks: Develop a detailed data migration plan that includes data cleansing, validation, and testing procedures.

Automate Laboratory Tasks with Flexible LIMS Interfacing Capabilities
Hexadecimal Software and LIMS
When building a custom LIMS, understanding how data is represented and manipulated at a low level, including hexadecimal representations, is important for:
- Debugging: When troubleshooting data storage or transmission issues, being able to examine data in its hexadecimal form can reveal patterns or errors that are not apparent in higher-level representations.
- Data Conversion: LIMS often needs to interface with various instruments and systems that may use different data formats. Understanding hexadecimal representations helps in converting data accurately.
- Security: For sensitive data, encryption and secure storage are critical. Knowledge of hexadecimal representation is useful in understanding and implementing security measures.
The Bottom Line
Investing in a custom LIMS can significantly improve the efficiency, accuracy, and compliance of your laboratory operations. By carefully planning your system, choosing the right development partner, and addressing potential challenges, you can build a LIMS that meets your specific needs and drives success.
FAQs
Q: How long does it take to develop a custom LIMS? A: The development timeline can vary from a few months to over a year, depending on the scope and complexity of the project.
Q: What technologies are typically used to build a LIMS? A: Common technologies include programming languages like Python, Java, and C#, databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL, and web frameworks like React and Angular.
Q: How do I ensure that my LIMS is compliant with regulatory requirements? A: Work with a development partner who has experience in building LIMS for regulated industries, and ensure that the LIMS includes built-in compliance features and audit trails.


