DLT Full Form: What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
Updated on : 14 April 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is like a digital notebook shared across a network—everyone has a copy, and no one can cheat. It’s secure, transparent, and tamper-proof, making it perfect for everything from cryptocurrency 💰 to supply chains The future runs on DLT! 🚀
What Is DLT?
Image Source: google
1. Definition 📌
- DLT is a digital system for recording the transaction of assets in which the transactions and their details are recorded in multiple places at the same time.
- No central data store or administration functionality.
2. Key Characteristics 🧠
- Decentralization: No central authority controls the ledger.
- Transparency: All participants have access to the same data.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded, it cannot be changed or deleted.
- Consensus Mechanism: Validates and agrees on entries across the network.
3. How It Differs from Traditional Databases 🔄
- Traditional: Centralized, single point of failure, easy to manipulate.
- DLT: Distributed, fault-tolerant, tamper-proof.
4. Components of DLT 🧩
- Ledger: The digital record of transactions.
- Nodes: Devices/participants in the network maintaining the ledger.
- Consensus Protocol: Rules that ensure agreement on the ledger state (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake).
5. Example Technologies Using DLT 🌐
- Blockchain: The most common type (used in Bitcoin, Ethereum).
- Hashgraph, DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph): Other forms of DLT.
6. Why It Matters 📈
- Enhances trust in digital transactions.
- Enables peer-to-peer interaction without intermediaries.
- Used in various fields like finance, healthcare, supply chain, and government.

Want to implement DLT in your enterprise solutions?
History of DLT
| Milestone | Description |
|---|---|
| Early Concepts (1990s) | The idea of distributed systems and cryptographic ledgers began gaining attention among computer scientists. |
| Bitcoin & Blockchain (2008) | Satoshi Nakamoto introduced Bitcoin and the first practical use of blockchain—a type of DLT. |
| Rise of Altcoins (2011–2015) | Other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum emerged, expanding DLT’s potential with smart contracts. |
| Enterprise Adoption (2016–2019) | Businesses began exploring private and consortium blockchains for supply chain, finance, and identity. |
| Beyond Blockchain (2020�–Present) | New forms of DLT like DAG and Hashgraph appeared, offering faster and more scalable alternatives. |
How DLT Works
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Distributed Network | DLT operates on a decentralized network of nodes, where each node holds a copy of the ledger. |
| Consensus Mechanism | Nodes reach consensus to validate and agree on transactions, ensuring data integrity. |
| Immutable Records | Once a transaction is added to the ledger, it cannot be altered, ensuring security and trust. |
| Cryptographic Security | DLT uses cryptographic algorithms to secure transactions and user identities. |
| Smart Contracts | DLT platforms like Ethereum allow programmable contracts that automatically execute when conditions are met. |
Types of DLT
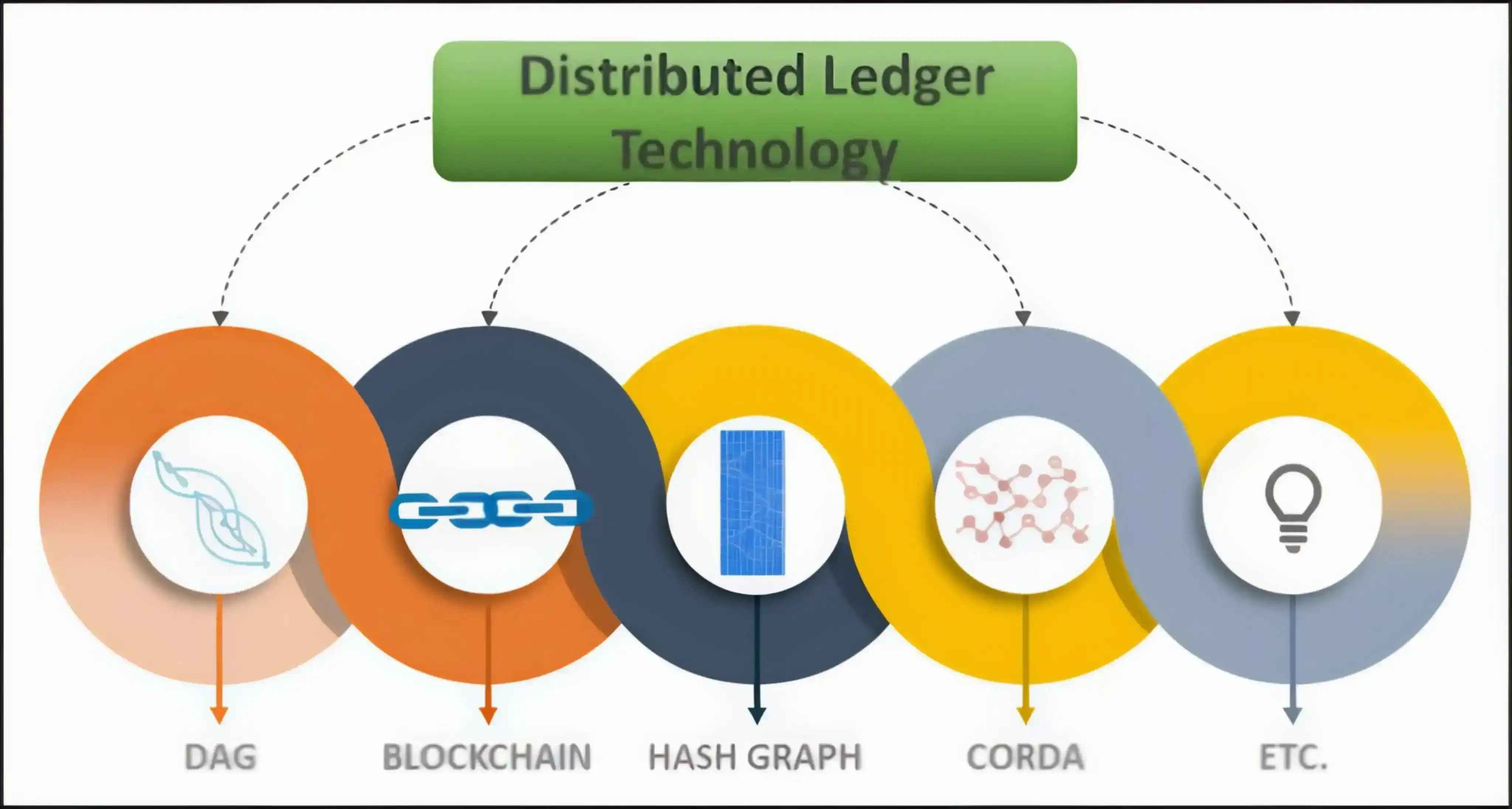
Image Source: google
- Blockchain ⛓️
-
Description: A blockchain is a chain of blocks where each block contains a list of transactions. It is the most widely known type of DLT, popularized by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
-
Key Features:
-
Immutable: Once a block is added, it cannot be changed or removed, ensuring data integrity.
-
Decentralized: No central authority; all nodes (computers) validate transactions.
-
Cryptographic Security: Transactions are secured through cryptographic methods like hashing.
-
Use Cases: Cryptocurrencies, supply chain tracking, voting systems.
- Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) 🔀
-
Description: Unlike blockchain, which forms a chain, DAG structures transactions as a graph where each transaction can reference multiple previous ones, creating a web-like structure.
-
Key Features:
-
No Miners: Unlike blockchain, DAG doesn’t require miners to validate transactions, which leads to lower fees and faster processing.
-
Scalability: DAG can handle a higher transaction throughput compared to traditional blockchain.
-
Lightweight: Suitable for devices with lower processing power, like IoT.
-
Use Cases: IOTA (Internet of Things), payment systems, microtransactions.
- Hashgraph 🌐
-
Description: Hashgraph is a consensus algorithm that is faster, more secure, and scalable than blockchain. It is based on a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure but operates differently to ensure high throughput.
-
Key Features:
-
Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT): Ensures security even when some nodes are compromised or behave maliciously.
-
Fast and Scalable: Hashgraph processes transactions faster than traditional blockchains.
-
Fairness: Transaction order is determined by the timestamp of the first node to see a transaction, preventing manipulation.
-
Use Cases: High-frequency financial transactions, enterprise solutions, smart contracts.
- Private and Permissioned Ledgers 🔒
-
Description : These ledgers are controlled by a central organization or a consortium of entities. Only authorized participants can access and update the ledger.
-
Key Features:
-
Control and Privacy: Access is restricted to trusted parties, and data privacy is maintained.
-
Faster Transactions: Since fewer nodes are involved, transactions can be validated more quickly.
-
Customizable Consensus Mechanisms: Organizations can choose the most suitable consensus model based on their needs.
-
Use Cases: Supply chains, healthcare, banking, and financial institutions.
- Public and Permissionless Ledgers 🌍
-
Description: These are open to anyone, and anyone can join the network, validate transactions, and participate in consensus. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples of public, permissionless ledgers.
-
Key Features:
-
Decentralization: No central authority governs the ledger, and anyone can participate.
-
Transparency: Transactions are visible to all network participants.
-
Security: Uses consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to ensure network integrity.
-
Use Cases: Cryptocurrencies, decentralized applications (DApps), decentralized finance (DeFi).
Smart Blockchain Solutions for Your Business with Hexadeciaml Software
DLT Consensus Mechanisms
| Consensus Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Proof of Work (PoW) | Nodes compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the ledger. The first to solve the puzzle gets a reward. |
| Proof of Stake (PoS) | Validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to 'stake' as collateral. |
| Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) | A variation of PoS where stakeholders vote for a small number of trusted validators who will validate transactions and create blocks. |
| Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) | Nodes in the network reach consensus through a voting process, ensuring that the system can tolerate up to one-third of faulty or malicious nodes. |
| Proof of Authority (PoA) | Validators are pre-approved and trusted entities that validate transactions and produce new blocks. This mechanism is faster but less decentralized. |
| Proof of Space (PoSpace) | Validators offer unused hard drive space as a proof of their commitment, and they are rewarded for storing data and validating blocks. |
| Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET) | Nodes wait for a randomly chosen time period to pass before they can validate a transaction, creating a fair and efficient consensus process. |
| Federated Consensus | A consensus model used by permissioned ledgers where a group of trusted nodes (called federated nodes) validates transactions collectively. |
Industries Using DLT
Image Source: google
| Industry | Use of DLT |
|---|---|
| Finance | DLT is used for secure and transparent transactions, cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum), and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. |
| Supply Chain | DLT provides transparency and traceability, helping companies track goods from origin to destination, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud. |
| Healthcare | DLT can securely store and share patient data, improve interoperability between systems, and enhance privacy and security. |
| Government | DLT is used for voting systems, identity management, land registration, and ensuring transparency in public records. |
| Energy | DLT enables peer-to-peer energy trading, improves the efficiency of energy distribution, and supports decentralized grids. |
| Retail | DLT facilitates secure transactions, enhances supply chain management, and allows for loyalty programs and digital payment systems. |
| Real Estate | DLT streamlines property transactions, reduces paperwork, and ensures transparent property ownership records. |
| Insurance | DLT can automate claims processing through smart contracts, reduce fraud, and improve customer trust in policy management. |
| Legal | DLT is used for creating and managing smart contracts, ensuring secure and transparent legal agreements. |
| Telecommunications | DLT is applied in managing data ownership, secure transactions, and billing systems in telecom networks. |

Explore Blockchain & DLT services by Hexadecimal Software
Uses of DLT
- Cryptocurrency and Digital Payments 💸
- What it does: DLT enables secure, peer-to-peer transactions without needing banks. It powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Why it matters: It allows for fast, low-cost, and transparent money transfers globally.
- Supply Chain Management 📦
- What it does: DLT helps track products from creation to delivery, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
- Why it matters: Companies can monitor the movement of goods in real-time, improving transparency and trust.
- Smart Contracts 🤖
- What it does: DLT allows contracts to automatically execute when conditions are met, without middlemen.
- Why it matters: This reduces delays, errors, and fraud in contracts (like legal agreements or insurance claims).
- Identity Management 🆔
- What it does: DLT securely manages digital identities, giving users control over their personal information.
- Why it matters: It provides more secure online identity verification, helping prevent identity theft.
- Voting Systems 🗳️
- What it does: DLT makes voting more secure, transparent, and tamper-proof.
- Why it matters: It ensures election results are accurate and transparent, reducing fraud.
- Healthcare Data Management 🏥
- What it does: DLT securely stores and shares health data between doctors, hospitals, and patients.
- Why it matters: It improves privacy, security, and coordination in patient care.
- Cross-Border Payments 🌍
- What it does: DLT simplifies international payments, making them faster and cheaper.
- Why it matters: It allows global transactions to happen in minutes with lower fees compared to traditional banking methods.
- Insurance 📑
- What it does: DLT automates insurance claims and reduces fraud by securely storing all transactions.
- Why it matters: Claims are processed faster and more accurately, improving customer trust.
- Intellectual Property Protection 🛡️
- What it does: DLT helps creators register and track their intellectual property (e.g., patents or copyrights).
- Why it matters: It proves ownership and ensures creators receive fair compensation for their work.
- Asset Tokenization 🏢
- What it does: DLT allows physical and digital assets to be divided into smaller, tradable parts (tokens).
- Why it matters: This makes assets more accessible for investment and improves liquidity in markets.
Pros and Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Decentralized – no single control | Can be slow depending on the consensus method |
| Improved transparency and trust | High energy use (e.g., in Proof of Work) |
| Tamper-proof and secure | Scalability issues for large networks |
| Reduces need for intermediaries | Regulatory uncertainty in some regions |
| Efficient record-keeping | Complex to implement and maintain |
Why DLT Is Important
| 📌 Reason | 📋 Explanation |
|---|---|
| Decentralization | No single authority controls the data. Everyone shares the same copy of the ledger. |
| Transparency & Trust | All transactions are visible to participants, increasing trust. |
| Security | Data is encrypted and tamper-proof, making it very secure. |
| Faster & Cheaper Transactions | Reduces delays and costs by removing intermediaries. |
| Smart Contracts | Automates tasks based on conditions, reducing errors and speeding up processes. |
| Data Integrity | Once recorded, data can’t be changed. Ensures accuracy and accountability. |
DLT vs Blockchain
Image Source: google
| 🔍 Feature | 📘 DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology) | 📗 Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A digital system to record data across multiple locations without a central authority. | A type of DLT where data is stored in blocks linked in a chain. |
| Structure | Can be any form (blockchain, DAG, etc.). | Specifically structured as a chain of blocks. |
| Block Concept | Does not always use blocks. | Always uses blocks to store data. |
| Examples | Blockchain, DAG (e.g., IOTA), Hashgraph. | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, etc. |
| Popularity | Broader term including all distributed ledgers. | Most well-known and widely used DLT type. |
| Use Cases | Finance, healthcare, supply chain, voting, etc. | Cryptocurrencies, NFTs, smart contracts, etc. |
Future of DLT
- Wider Adoption Across Industries
- More businesses, governments, and sectors (like finance, healthcare, and logistics) will use DLT for transparency and efficiency.
- Scalability Improvements
- Newer DLT models (like DAG and Hashgraph) will solve speed and scalability issues seen in older systems.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies
- DLT will work alongside AI, IoT, and 5G for smarter automation, real-time data sharing, and secure transactions.
- Stronger Regulations and Standards
- Governments are expected to create clear rules to ensure safe and legal use of DLT worldwide.
- Decentralized Applications (DApps) Growth
- Apps built on DLT (like DeFi and decentralized identity) will grow, offering users more control and privacy.
- More User-Friendly Platforms
- Future DLT platforms will be easier to use, making adoption simpler for both businesses and individuals.
FAQs
Q.1. What is Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)?
A : DLT is a digital system for recording transactions and data across multiple computers (nodes) without a central authority. All records are shared, synchronized, and secured.
Q.2. How is DLT different from Blockchain?
A : Blockchain is a type of DLT that stores data in blocks linked in a chain. DLT is a broader term that includes other formats like DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) and Hashgraph.
Q.3. What are the main benefits of DLT?
A : Transparency
A : Security
A : Decentralization
A : Faster and cheaper transactions
A : Reduced fraud and errors
Q.4. Where is DLT used in real life?
A : Cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum)
A : Supply chain tracking
A : Healthcare data sharing
A : Identity verification
A : Voting systems
A : Insurance and banking
Q.5. Is DLT secure?
A : Yes. DLT uses encryption and consensus mechanisms (like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) to secure data and prevent tampering.
Q.6. Can DLT be used without cryptocurrency?
A : Yes. DLT can be used for data sharing, identity management, supply chains, and more—without involving cryptocurrencies.
Q.7. What are smart contracts in DLT?
A : Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on a DLT that run automatically when certain conditions are met.
Q.8. What is a node in DLT?
A : A node is a computer that participates in the DLT network by storing and validating a copy of the ledger.
Q.9. Is DLT legal?
A : Yes, DLT is legal in most countries, but regulations are still developing in many places depending on its use (e.g., crypto, finance).
Q.10. What is the future of DLT?
A : DLT is expected to become more scalable, user-friendly, and widely used in business, government, and daily life.


