MySQL vs SQL: Key Differences Explained
Updated on : 29 April 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. SQL vs NoSQL: Whats the Real Difference?
- 3. Understanding Databases: A Beginners Guide
- 4. Exploring Types of Databases and Their Uses
- 5. Relational Databases Explained Simply
- 6. Introduction to SQL: The Query Language of Data
- 7. What Is SQL Server and How Does It Work?
- 8. Getting to Know MySQL: Features and Benefits
- 9. Using SQL in MySQL: A Practical Guide
- 10. SQL vs MySQL: Key Comparisons You Should Know
- 11. Is SQL Compatible With All Databases?
- 12. Using SQL Across Multiple Database Systems
- 13. Do All Databases Speak SQL? Debunking the Myth
- 14. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Ever wondered how websites store your data? 🤔 Meet SQL 🧠—the universal language of databases—and MySQL 💾, the powerful engine that speaks it. Knowing the difference between the two can supercharge your database skills 🚀 and open doors to smarter data handling! 🔓📊
SQL vs NoSQL: Whats the Real Difference?

Image Source: google
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| Data Model | SQL uses structured tables with fixed schemas; NoSQL uses flexible, varied data models (document, key-value, graph, etc.) |
| Scalability | SQL scales vertically (stronger server); NoSQL scales horizontally (more servers) |
| Query Language | SQL uses Structured Query Language; NoSQL uses diverse APIs and query methods |
| Schema | SQL requires predefined schema; NoSQL allows dynamic schema for unstructured data |
| Best For | SQL suits complex queries & transactions; NoSQL fits large-scale, rapidly changing data |
Understanding Databases: A Beginners Guide
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A database is an organized collection of structured information, stored electronically. |
| Purpose | Helps store, manage, and retrieve data efficiently. |
| Types | Includes relational, NoSQL, hierarchical, and network databases. |
| Components | Key parts include tables, queries, forms, and reports. |
| Users | Used by developers, analysts, and applications to handle data. |

you want to hire SQL Developer?
Exploring Types of Databases & Their Uses
1. Relational Databases (RDBMS) 🗂️
- Stores data in tables with rows and columns.
- Uses SQL for querying.
- Best for: Structured data, complex queries, and transactions.
Example: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle.
2. NoSQL Databases 📄
- Includes document, key-value, column, and graph models.
- Schema-less and highly flexible.
- Best for: Big data, real-time applications, unstructured data.
Example: MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis.
3. Hierarchical Databases 🌳
- Data is organized in a tree-like structure.
- Parent-child relationships dominate.
- Best for: Applications with a clear hierarchy.
Example: IBM Information Management System (IMS).
4. Network Databases 🔗
- More flexible than hierarchical, with multiple parent-child links.
- Uses sets to define relationships.
- Best for: Complex data relationships.
Example: Integrated Data Store (IDS).
5. Object-Oriented Databases 🧱
- Stores data as objects, like in object-oriented programming.
- Supports complex data types.
- Best for: Applications that require storing multimedia or complex structures.
Example: db4o, ObjectDB.
Relational Databases Explained Simply
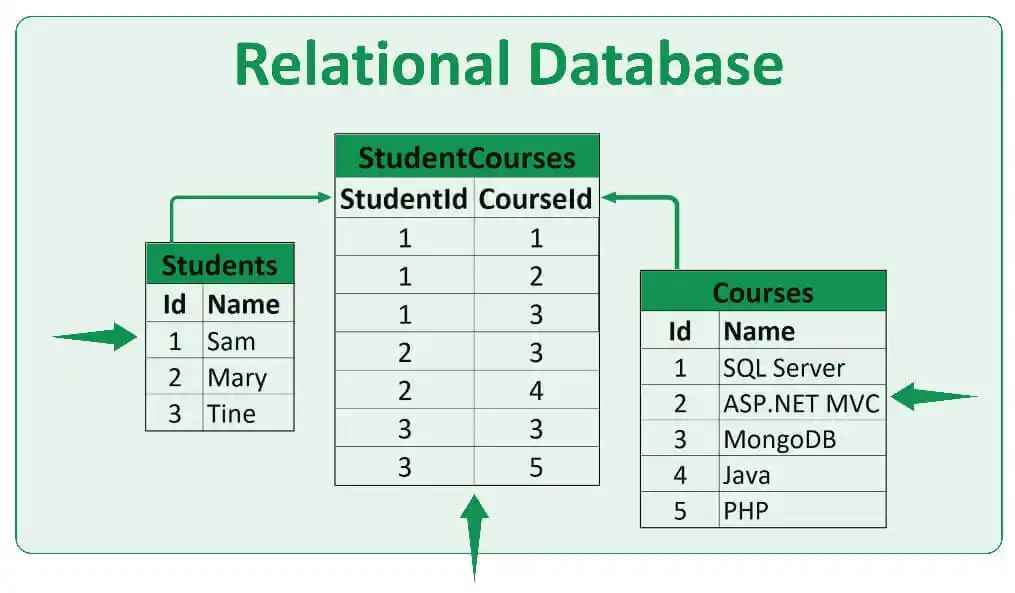
Image Source: google
What They Are
- A relational database stores data in tables (also called relations) with rows and columns.
How They Work
- Each row represents a record.
- Each column represents a field or attribute.
- Tables can be linked using keys (primary & foreign).
Why Use Them?
- Easy to organize and retrieve data using SQL.
- Ensure data integrity with constraints and relationships.
- Ideal for structured data like user profiles, orders, inventory, etc.
Examples
- Popular systems: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL.
Best For
- Applications that require complex queries, data consistency, and transactions.
Introduction to SQL: The Query Language of Data
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| What it is | SQL (Structured Query Language) is a language used for managing and manipulating structured data in relational databases. |
| How it works | SQL uses predefined schemas, tables, and relationships to manage data and supports operations like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE. |
| When to use | When data is highly structured, consistent, and follows a tabular format, such as financial, transactional, or inventory systems. |
| Requirement | Requires a relational database with a defined schema and structured data. |
| Action | Data is stored in tables with rows and columns, and SQL is used to query and manipulate the data through defined commands. |
You Might Also Like
What Is SQL Server and How Does It Work?
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| What it is | SQL Server is a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft for storing and managing data. |
| How it works | SQL Server uses a client-server architecture, where the SQL Server instance handles database operations and the client requests the data using SQL commands. |
| Core components | Core components include the Database Engine, SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), and SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS). |
| When to use | Used when you need a reliable, scalable, and secure database solution for managing structured data in enterprise-level applications. |
| Data Storage | SQL Server stores data in tables with rows and columns, and it enforces constraints to maintain data integrity. |
| Key Features | Includes powerful features like data encryption, high availability (Always On), full-text search, and indexing for performance optimization. |
| Action | Data is manipulated using Transact-SQL (T-SQL) commands, which are processed by the SQL Server engine to execute operations on the database. |

Looking mySQL Developer For your business?
Getting to Know MySQL: Features and Benefits
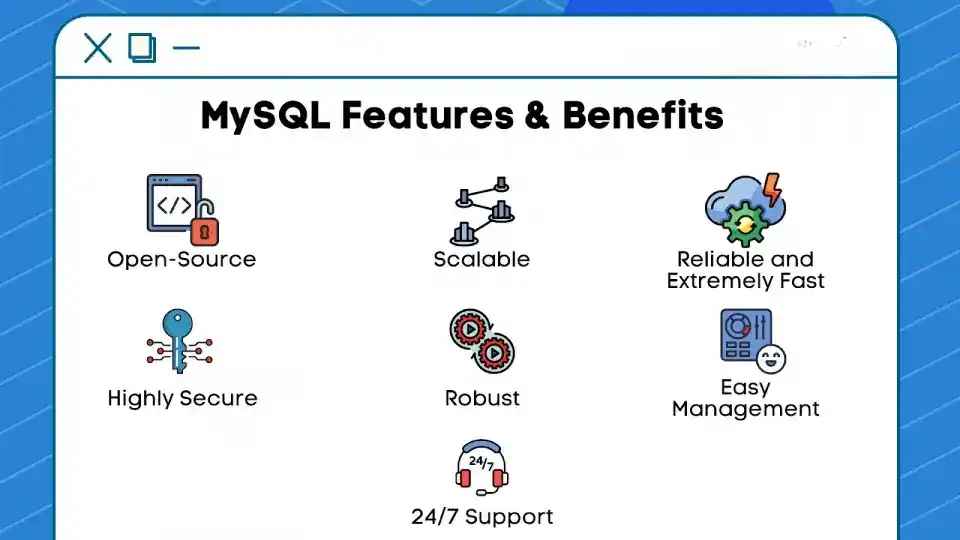
Image Source: google
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| What it is | MySQL is an open-source database system used to store and manage data. |
| Key Features | 1. Free and Open Source 🆓 2. Works Everywhere 🌐 3. Fast and Efficient ⚡ 4. Scalable 📈 5. Reliable Transactions ✅ 6. Secure 🔒 |
| Benefits | 1. Low Cost 💰 2. Easy to Use 🖥️ 3. Community Support 🤝 4. Flexible 🔄 5. Widely Used 🌍 |
| Why Use MySQL? | Fast, reliable, and free. Ideal for small and large applications, offering security and efficiency. |
Using SQL in MySQL: A Practical Guide
🔍 1. Basic SQL Commands
-
SELECT 🧐
- Retrieves data from one or more tables.
- Example:
SELECT * FROM users;
-
INSERT ➕
- Adds new records into a table.
- Example:
INSERT INTO users (name, age) VALUES ('John', 25);
-
UPDATE ✏️
- Modifies existing records in a table.
- Example:
UPDATE users SET age = 26 WHERE name = 'John';
-
DELETE ❌
- Removes records from a table.
- Example:
DELETE FROM users WHERE name = 'John';
🔧 2. Working with Conditions
-
WHERE 📍
- Filters records based on specific conditions.
- Example:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE age > 20;
-
AND / OR 🔗
- Combines multiple conditions.
- Example:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE age > 20 AND name = 'John';
📊 3. Sorting and Limiting Results
-
ORDER BY 🔠
- Sorts records in ascending or descending order.
- Example:
SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY age DESC;
-
LIMIT ⏳
- Limits the number of records returned.
- Example:
SELECT * FROM users LIMIT 5;
🔗 4. Joins in SQL
-
INNER JOIN 🔗
- Combines rows from two or more tables based on a related column.
- Example:
SELECT users.name, orders.amount FROM users INNER JOIN orders ON users.id = orders.user_id;
-
LEFT JOIN 👈
- Returns all records from the left table and matched records from the right table.
- Example:
SELECT users.name, orders.amount FROM users LEFT JOIN orders ON users.id = orders.user_id;
🔒 5. Grouping and Aggregation
-
GROUP BY 🗂️
- Groups rows that have the same values into summary rows.
- Example:
SELECT age, COUNT(*) FROM users GROUP BY age;
-
HAVING 🎯
- Filters records after aggregation.
- Example:
SELECT age, COUNT(*) FROM users GROUP BY age HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
📝 6. Subqueries and Nested Queries
- Subqueries 🔄
- A query inside another query. Often used in the WHERE clause.
- Example:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE age > (SELECT AVG(age) FROM users);
💡 7. Creating and Modifying Tables
-
CREATE TABLE 🛠️
- Creates a new table in the database.
- Example:
CREATE TABLE users (id INT, name VARCHAR(100), age INT);
-
ALTER TABLE ⚙️
- Modifies an existing table.
- Example:
ALTER TABLE users ADD email VARCHAR(100);
-
DROP TABLE 🗑️
- Deletes a table from the database.
- Example:
DROP TABLE users;
🚀 8. Indexing for Performance
- CREATE INDEX 🔍
-
Creates an index on one or more columns to improve query performance.
-
Example:
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON users(name);
-
SQL vs MySQL: Key Comparisons You Should Know
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 SQL | 📝 MySQL |
|---|---|---|
| What it is | SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standard language for managing relational databases. | MySQL is an open-source database system that uses SQL as its query language. |
| Type | SQL is a language used for querying and managing databases. | MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that stores and manages data. |
| Usage | SQL is used for writing queries, managing data, and defining database structures. | MySQL is used for storing data and running SQL queries to retrieve or manipulate it. |
| License | SQL is a standardized language and doesn’t have a license. | MySQL is open-source and distributed under the GPL license. |
| Platform | SQL can be used across various database systems (e.g., Oracle, SQL Server). | MySQL is a specific RDBMS and is used on multiple platforms (Windows, Linux, etc.). |
| Performance | SQL performance depends on the underlying database system. | MySQL is known for its fast performance, especially with read-heavy applications. |
| Scalability | SQL itself is not scalable; the scalability depends on the database used. | MySQL is scalable and suitable for both small and large applications. |
| Security | SQL security is managed by the database system. | MySQL offers built-in security features like SSL, data encryption, and user authentication. |
Do you want to know about databases?
Is SQL Compatible With All Databases?
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 SQL Compatibility |
|---|---|
| What it is | SQL is a language used to manage and manipulate relational databases. |
| Compatibility | SQL is compatible with most relational databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server). |
| Notable Exceptions | SQL may not be directly compatible with NoSQL databases (e.g., MongoDB, Cassandra). |
| Portability | SQL commands may vary slightly across different database systems, but the core syntax remains consistent. |
| Limitations | Some database systems may implement SQL differently (e.g., Microsoft SQL Server uses T-SQL). |
Using SQL Across Multiple Database Systems
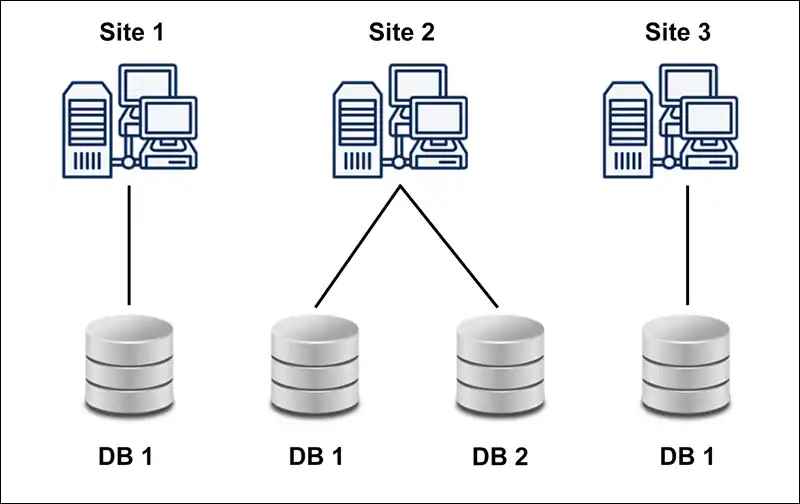
Image Source: google
- SQL is Cross-Platform 🌍
- SQL is designed to work across different relational database management systems (RDBMS), making it versatile and compatible with various platforms.
- Consistency in Syntax 📝
- Most relational databases use SQL with a consistent syntax, allowing for ease of use across different systems, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server.
- Differences in SQL Implementations 🔄
While SQL's core syntax remains consistent, specific implementations may vary:
- T-SQL (SQL Server) ⛓️
- PL/SQL (Oracle) 🔐
- PostgreSQL has additional features that differ from MySQL 🛠️.
- Portability Across Systems 🔁
- SQL queries can often be ported from one database to another, but adjustments might be needed due to slight variations in data types or functions.
- Vendor-Specific Features 🏷️
- Some databases offer proprietary features or extensions to SQL that may not be supported by other systems, which can affect portability.
- Database Migration Tools ⚙️
- Tools like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) help migrate SQL queries and data between different RDBMS while maintaining compatibility.
Do All Databases Speak SQL? Debunking the Myth
- SQL and Relational Databases 🗃️
- SQL is used by relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL to manage structured data.
- Not All Databases Use SQL ❌
- NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Redis do not use SQL. They have their own query languages.
- SQL vs. NoSQL 🔄
- SQL databases work with structured data in tables.
- NoSQL databases handle unstructured or flexible data.
- SQL is for Structured Data 🗂️
- SQL is best for structured data, but not for things like documents or key-value pairs.
- NoSQL Query Languages 🔍
- NoSQL databases use languages like MQL for MongoDB or CQL for Cassandra, not SQL.
- Some NoSQL Databases Use SQL-Like Queries ⚙️
- Some NoSQL databases (e.g., Cassandra, MongoDB) have SQL-like languages but they are different from traditional SQL.
- Why the Confusion? 🤔
- People often think all databases use SQL because it's so common with relational databases, but NoSQL databases are different.
FAQs
Q.1. What is SQL?
A : SQL (Structured Query Language) is a language used to manage and query relational databases.
Q.2. What is MySQL?
A : MySQL is a specific database management system that uses SQL to manage and store data.
Q.3. Is SQL a database?
A : No, SQL is a language, not a database. It’s used to interact with databases.
Q.4. Is MySQL a type of SQL?
A : No, MySQL is an open-source database system that uses SQL as its query language.
Q.5. Can I use SQL with MySQL?
A : Yes, MySQL uses SQL to perform database operations like querying, updating, and deleting data.
Q.6. Can SQL be used with other databases?
A : Yes, SQL can be used with many other relational databases like PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and Oracle.
Q.7. Are MySQL and SQL the same thing?
A : No, SQL is the language used for database management, while MySQL is a specific database system that uses SQL.
Q.8. Which is better, MySQL or SQL?
A : Its not about better or worse. SQL is a language, while MySQL is a database system that uses SQL. They serve different purposes.





