What is the Internet of Things (IoT)? A Beginner's Guide
Updated on : 21 November, 2024, 12:20 IST
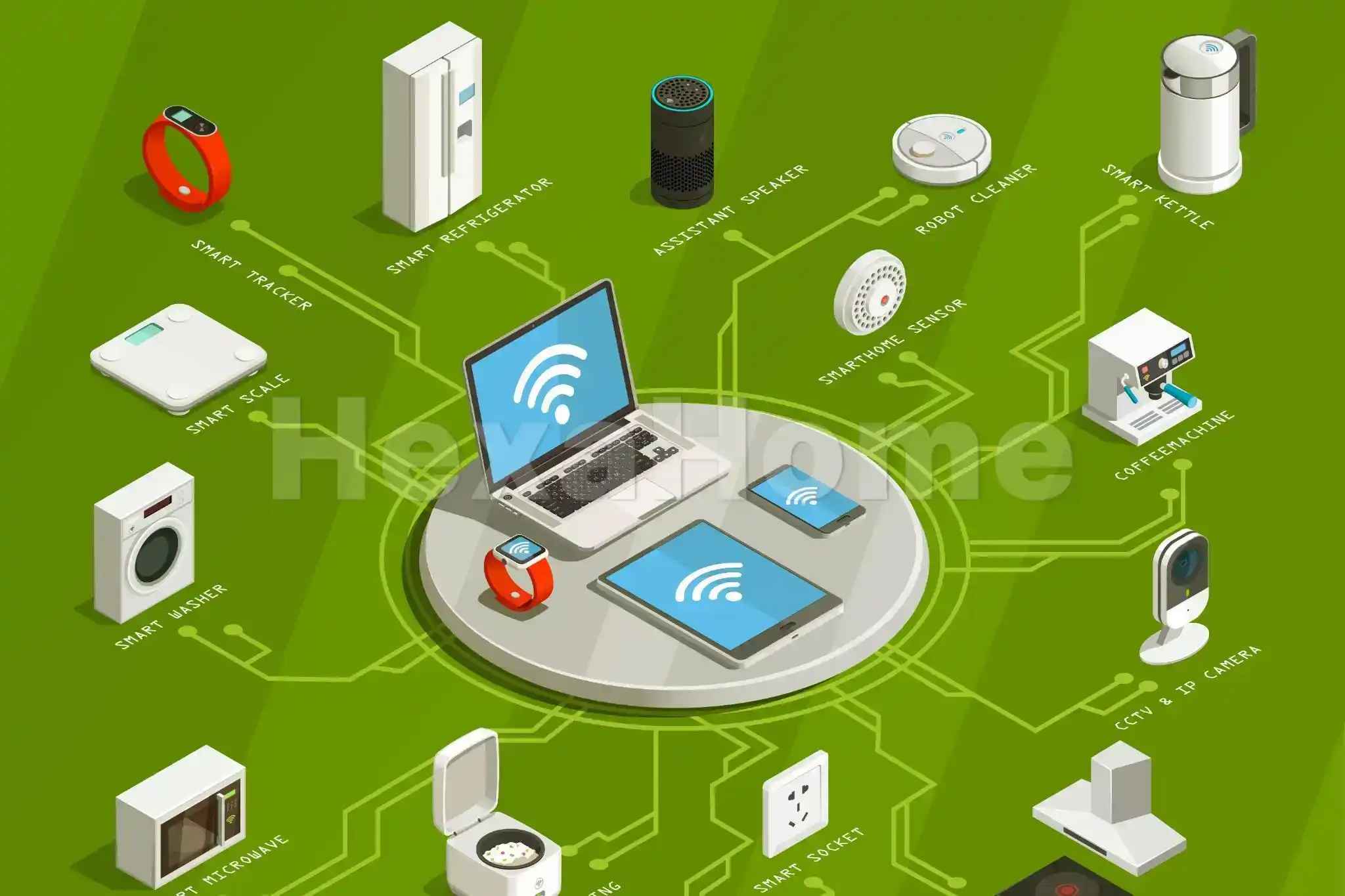
Image Source: Freepik
Table Of Contents
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly evolving technological paradigm that connects everyday objects to the internet, enabling them to send and receive data. This interconnected network of devices transforms how we live and work, making our environments smarter and more efficient. In this beginner's guide, we will explore what IoT is, how it works, its applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Understanding IoT?
At its core, IoT refers to a network of physical devices—ranging from household items like smart thermostats and refrigerators to industrial machinery—equipped with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities. These devices collect data from their environment and communicate with other devices or centralized systems over the internet. The primary goal of IoT is to improve efficiency and enhance user experiences by automating processes and providing real-time insights.
Key Components of IoT
-
Devices/Sensors: These are the physical objects that gather data from their surroundings. Examples include temperature sensors in smart thermostats or motion detectors in security systems.
-
Connectivity: Devices connect to the internet using various communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or cellular networks. This connectivity allows for data exchange between devices and centralized systems.
-
Data Processing: Once data is collected, it is processed either in the cloud or at the edge (near the source) to extract meaningful insights. This processing can involve analyzing patterns or identifying anomalies.
-
User Interface: Users interact with IoT systems through applications or dashboards that present data in an understandable format, allowing for informed decision-making.
How IoT Works
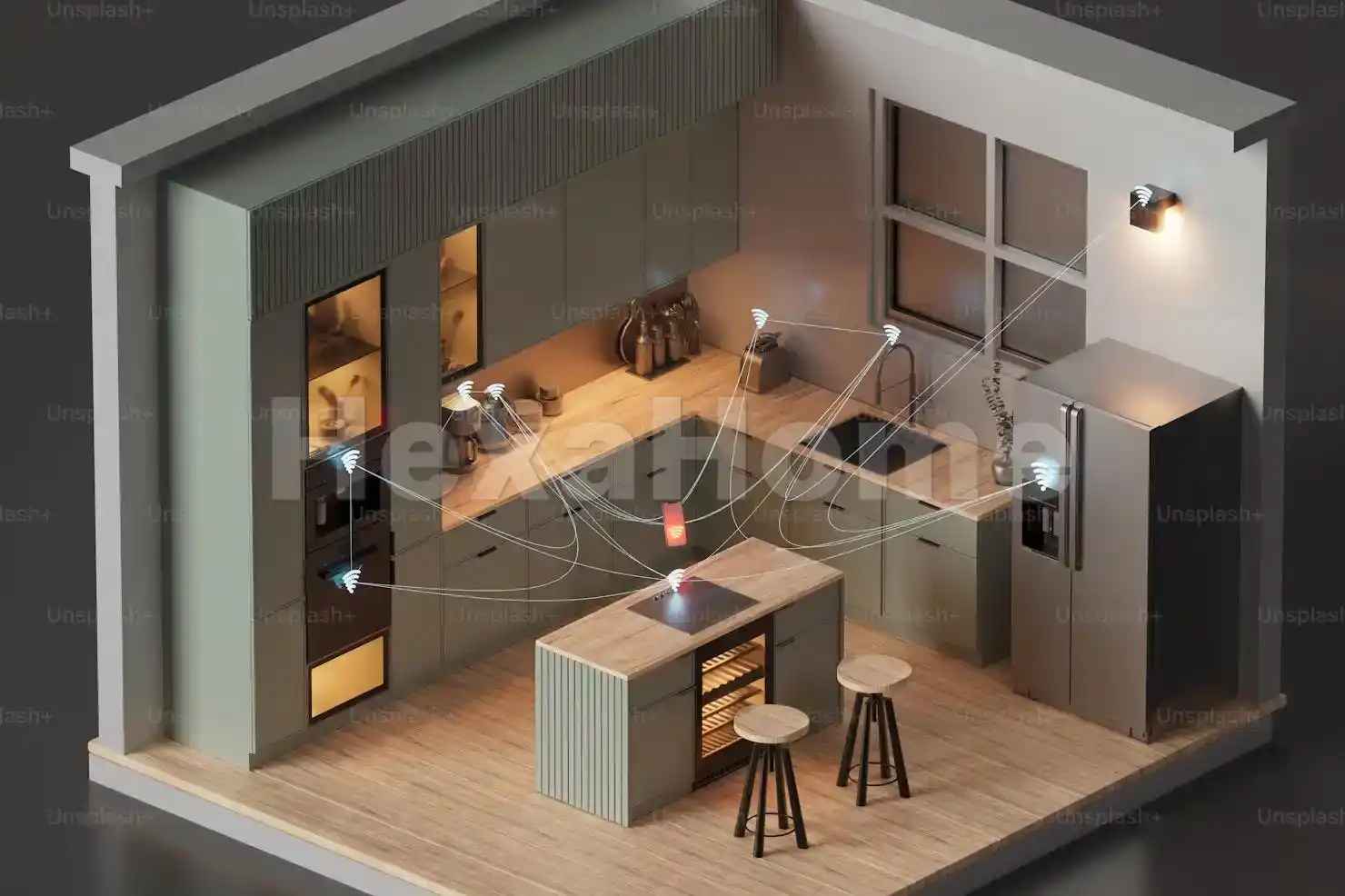

Image Source: unsplash.com
The operation of IoT can be broken down into several steps:
-
Data Collection: Sensors embedded in devices collect data from their environment.
-
Data Transmission: The collected data is sent to a cloud server or edge device for processing via internet connectivity.
-
Data Processing: The server processes the incoming data to analyze trends, identify issues, or generate actionable insights.
-
User Interaction: Users access this processed information through applications or dashboards, allowing them to monitor conditions, control devices remotely, or receive alerts.
Applications of IoT
The applications of IoT span various industries and everyday life:
-
Smart Homes: IoT technology enhances home automation through devices like smart thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras. Homeowners can control these devices remotely via smartphone apps, improving convenience and energy efficiency.
-
Healthcare: In healthcare, IoT enables remote patient monitoring through wearable devices that track vital signs such as heart rate and blood pressure. This real-time data allows healthcare providers to offer personalized treatment plans and timely interventions.
-
Industrial IoT (IIoT): IIoT focuses on improving manufacturing processes through connected machinery that monitors performance and predicts maintenance needs. This proactive approach reduces downtime and enhances operational efficiency.
-
Agriculture: IoT applications in agriculture include precision farming techniques where sensors monitor soil moisture levels and weather conditions. This data helps farmers optimize irrigation schedules and improve crop yields while conserving resources.
-
Smart Cities: Cities are increasingly adopting IoT solutions for better urban management. Applications include smart traffic lights that adjust based on real-time traffic conditions and waste management systems that optimize collection routes based on bin fill levels.
Benefits of IoT
The integration of IoT technology offers numerous advantages:
- Improved Efficiency: Automation of routine tasks reduces manual labor and optimizes resource utilization. Real-Time Data Insights: Access to real-time data enables informed decision-making and timely responses to issues.
- Cost Reduction: Predictive maintenance helps prevent costly downtimes by addressing equipment issues before they escalate.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalized services based on customer behavior analysis improve engagement and satisfaction.
- Sustainability: IoT solutions can optimize energy consumption and reduce waste, contributing to environmental sustainability efforts.
Challenges Facing IoT
Despite its potential benefits, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of IoT:
-
Security Risks: As more devices connect to the internet, the risk of cyberattacks increases. Ensuring robust security measures is crucial for protecting sensitive data.
-
Interoperability Issues: The diversity of devices from various manufacturers can lead to compatibility challenges within IoT ecosystems.
-
Data Privacy Concerns: The collection of vast amounts of personal data raises concerns about privacy and how this information is used.
-
Scalability: As organizations scale their IoT deployments, managing a growing number of connected devices can become complex.
Future Trends in IoT
The future of IoT holds exciting possibilities as technology continues to evolve:
-
Edge Computing: Processing data closer to where it is generated (edge computing) reduces latency and bandwidth usage, enhancing real-time decision-making capabilities.
-
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI will play a pivotal role in analyzing the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, enabling predictive analytics and automated responses.
-
Increased Adoption Across Industries: As technology matures, more sectors will adopt IoT solutions for improved operational efficiency and customer engagement.
-
Focus on Sustainability: Organizations will increasingly leverage IoT technologies to meet sustainability goals by optimizing resource use and reducing environmental impact.
-
Smart Cities Development: Continued investment in smart city initiatives will enhance urban living through improved infrastructure management and citizen services.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things represents a significant shift in how we interact with technology in our daily lives and across industries. By connecting physical objects to the internet, IoT enhances efficiency, improves decision-making processes, and transforms customer experiences. While challenges remain regarding security and interoperability, the potential benefits far outweigh these concerns as we move towards a more connected future.
As individuals become more familiar with smart technologies in their homes and workplaces, understanding the fundamentals of IoT will empower them to leverage its capabilities effectively. Whether it’s through improved health monitoring or enhanced automation at work, embracing the Internet of Things will undoubtedly shape our world for years to come.


